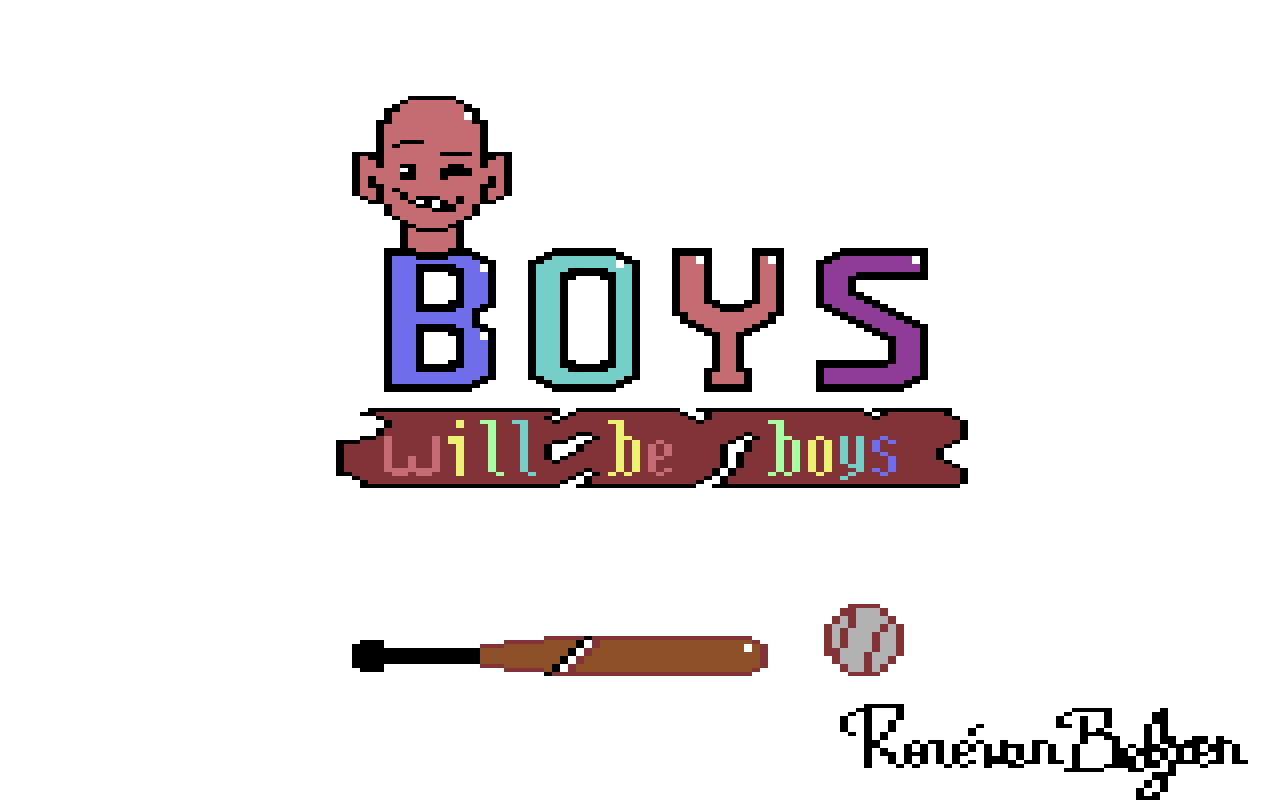-
Work in progress. I’m working with a mouse in Multipaint on my RPi.
What is he so happy about? I know, and you may too, once I’m done pushing pixels and uploaded it to my blog.
👾
-
A “little” thing as a broken iPad won’t stop me from making art. I made this when the iPad was almost gone.

And the other piece I made with a PETSCII editor on my RPi, based on a piece I did earlier this month.

Not having a backup for my Raspberry Pi makes me a bit nervous, as it should
🎨🐱👨💻🕹️👾 -
And my iPad gave up the ghost for good, meaning it’s in a continuous reboot cycle. I suspect the battery is no longer able to run the OS. I guess I’ll have to buy a new one next week, since I don’t want to replace the battery. The device no longer suited my needs anyway.
-
Analyzing @hutaffe’s (free) avatar from Make A pirate was a bit convoluted on my part…
Anyway, 100 by 100 pixel art, scaled up 8 times, with 53 unique colors, in isometric perspective, so typical for 2D games nowadays.
There’s a story here, stereotypical even, though better than I can ATM. 💡👾


-
This was taxing my iPad. Youtube in Safari with adblocker as picture in picture on top of a drawing app. The strokes had to be placed tactically to allow for overall sluggishness. Also, very distractive drawing and watching a video.
🎨👨💻📺
-
As Hanna-Barbera cartoons of the eighties have taught us, cats can without most clothes, except the most essential, like a hat or a cane.
🎨🐱👨💻🕹️👾
-
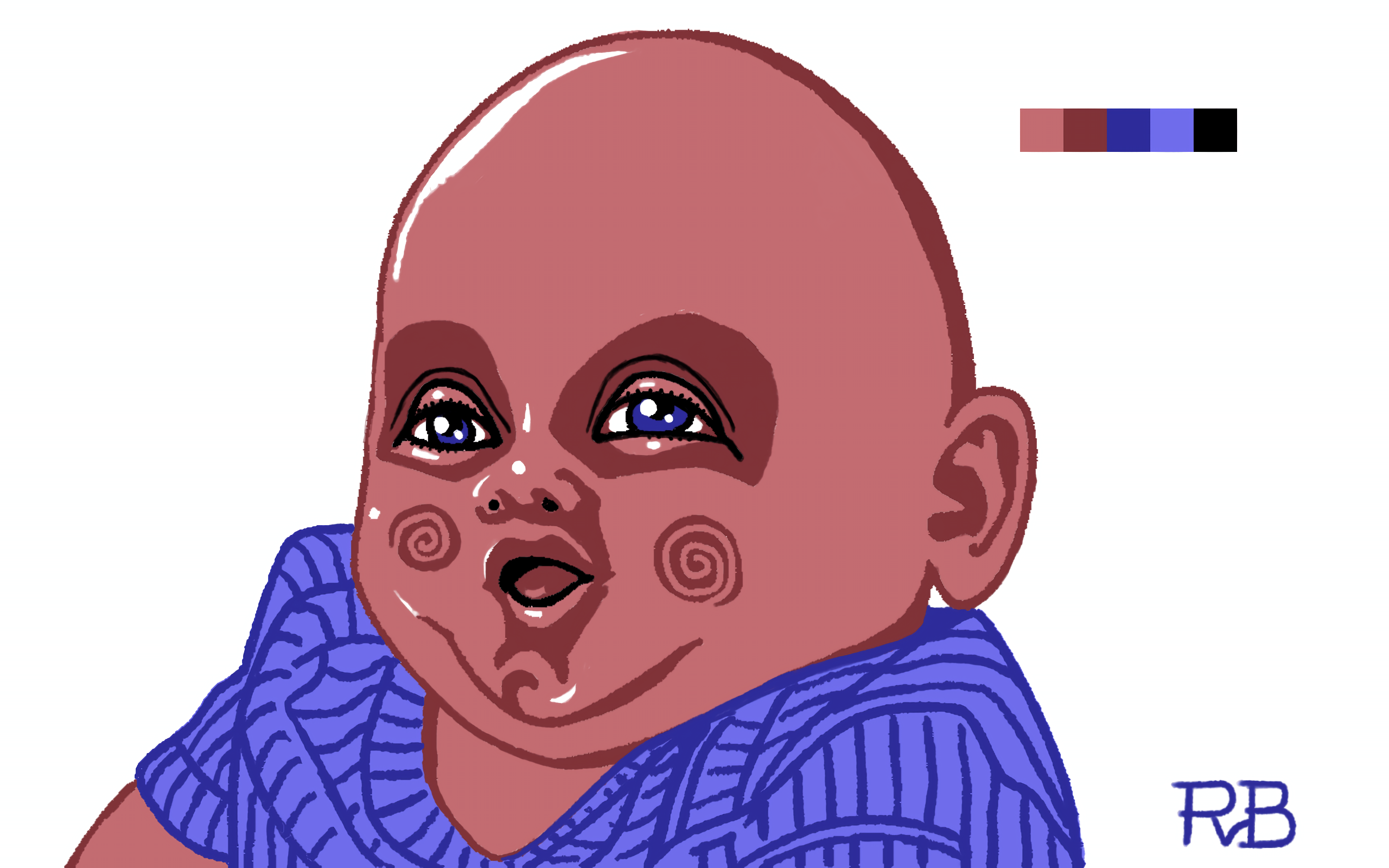
Sometimes limitation breeds creativity; usually frustration, though. The latter is often left out, rationalizing it as “part of the process.”
Drawn, but not copied 😇, from a photo. Six-color palette based on C64 colors. Drawn in ibisPaint X in roughly 5 hours, including a failed attempt.
🎨
-
While sketching this kitten I wondered how I could do away with all those lines. So I tried to eliminate as much as I dared. I’m sure more could be removed still. However, now the result was pretty “bland.” I suppose color has to do the brunt of the work, and there is too little of that.
🎨🐱

-
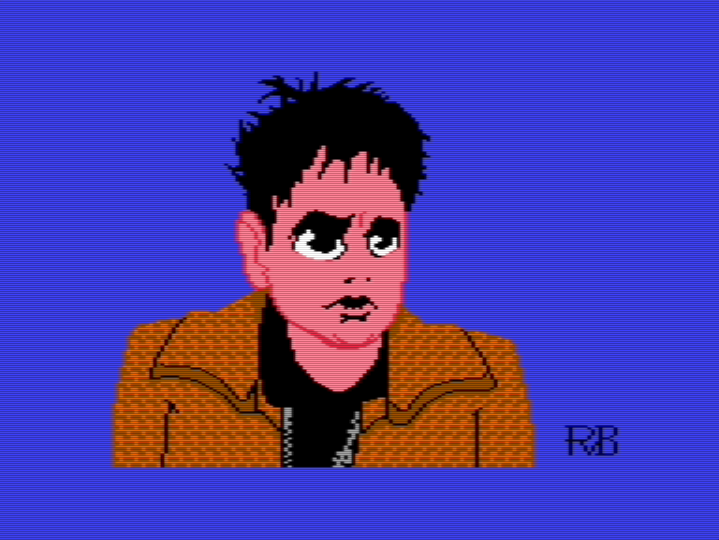
I find it always such a surprise how a pixel art drawing I made subtly (or sometimes radically) changes to conform to the rigors of the C64 multicolor bitmap.
Other than that, I used some of the edging techniques (sharp, lost and soft edges). So there’s that too. Happy 😊 camper here!
🎨👽👨💻🕹️👾
-
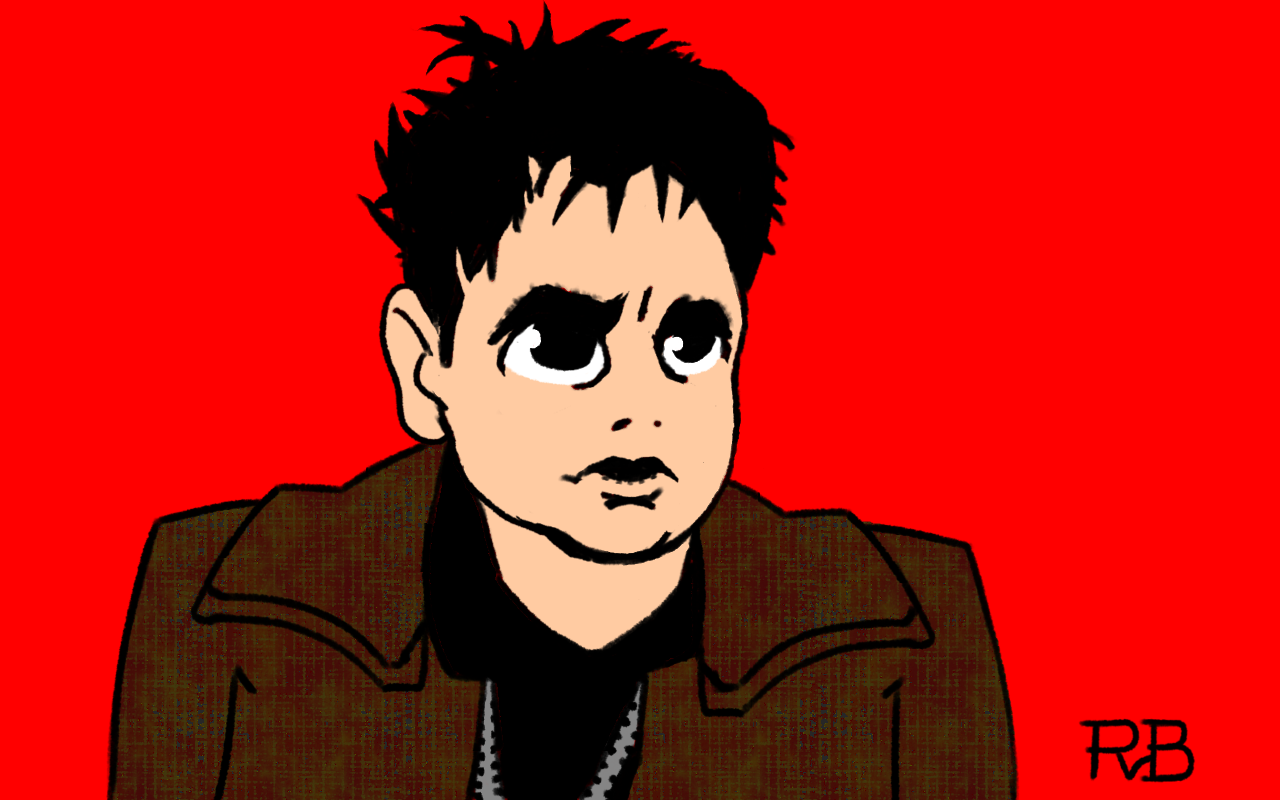
I was listening to a podcast about Blade Runner (1982), which inspired me to draw Rick Deckard, as played by Harrison Ford. Took me 1½ hours.
-
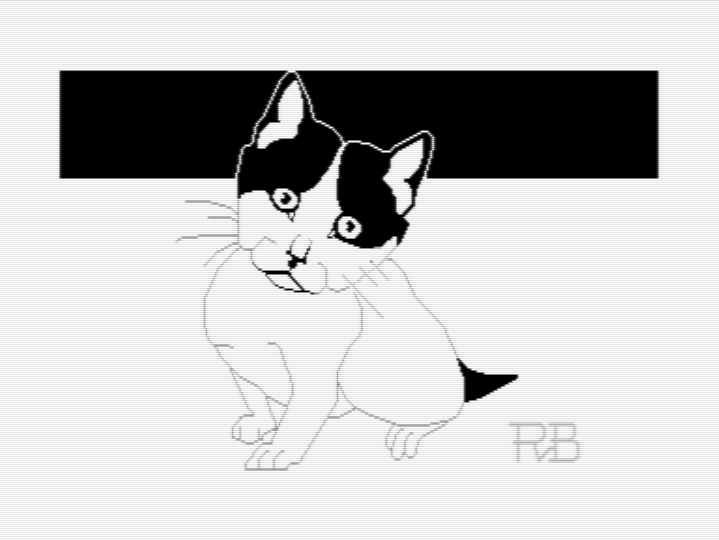
Searching on Flickr for Creative Commons photos of kittens I found this cute black and white one. I used it as reference for my C64 hi-res bitmap pixel art drawing.
Sometimes less color is better. Especially if the one depicted is staring into your soul.
🎨👨💻👾🕹️🐱😈
-
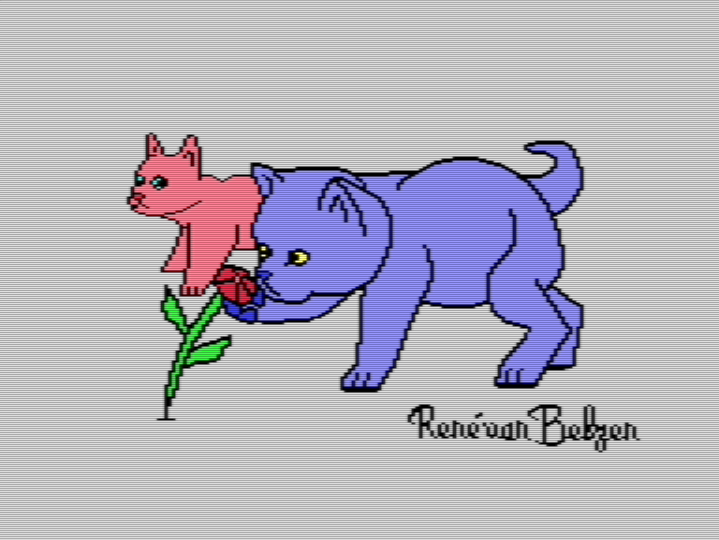
I didn’t get to experiment with edges. Still, I drew something I love, so that’s good.
Maybe advice from an oil painter doesn’t translate all that well to pixel art. Pixel art has more in common with decorative art (like embroidery) than with traditional art you can hang on a wall.
🎨🐱👨💻🕹️👾
-
Sometimes (read: often) I get distracted by an interesting bit of art-making fundamentals, try to apply it, then get totally side-stepped by the intracies of drawing from a cute photo, forgetting what I wanted to try out in the first place. The creative process never seems to go in a straight line.
🎨
-
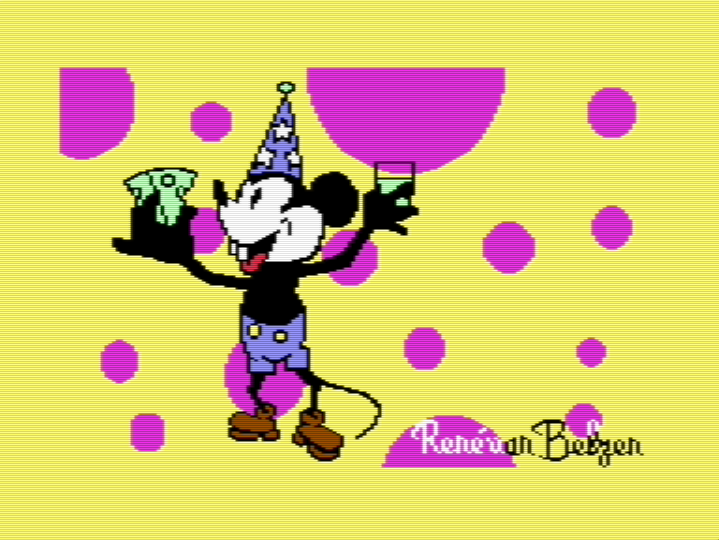
Public domain now?
🎨👨💻🕹️👾

-
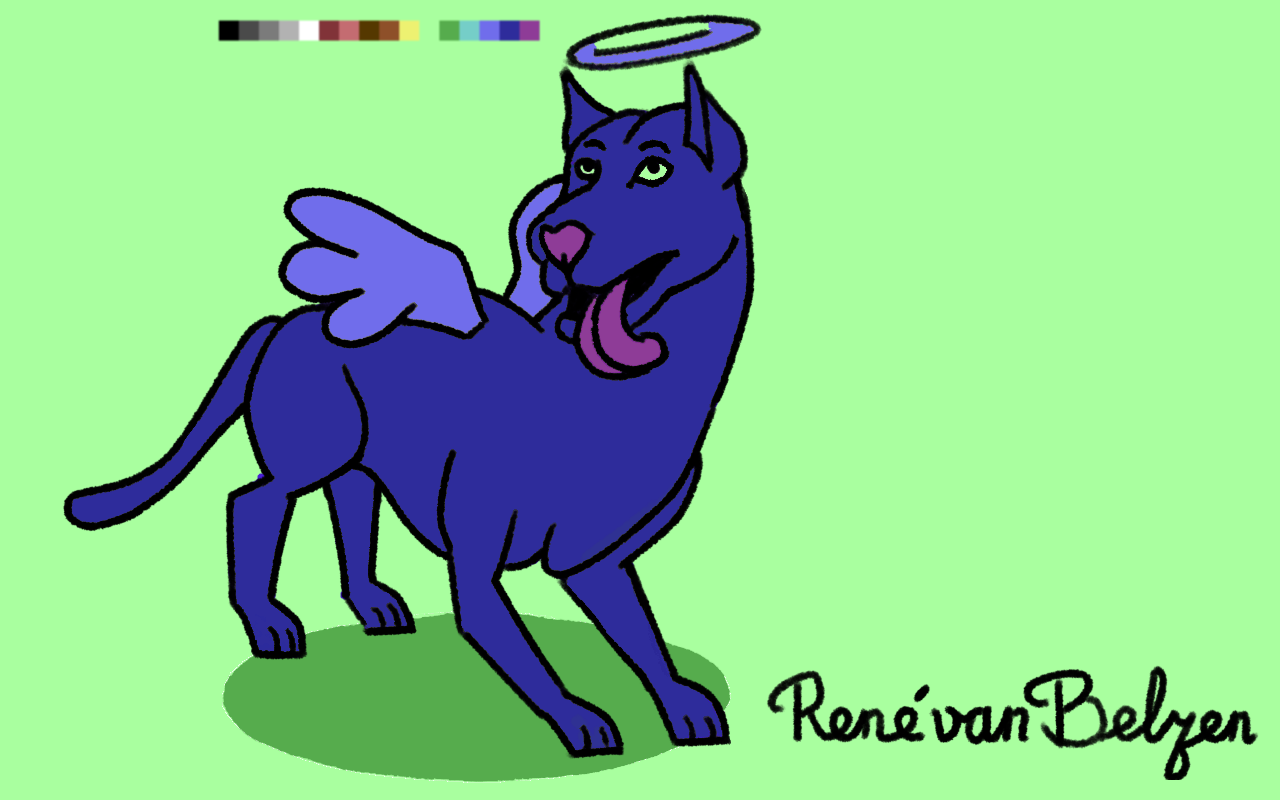
It is said all dogs go to the Good Place.
Drawn in ibisPaint X on 9th gen iPad with first gen Apple Pencil.
🐶🎨
-
For this piece of pixel art I called upon my knowledge of the Period Table of Elements for illustrating the Pixel Dailies prompt for January 12, 2024, “Golden.”

-
I suppose the lesson to be learned here is:
Don’t look into the spiral, or you’ll go cuckoo, bananas, Dada
A quick peek is no problem, though.
🎨👨💻🕹️👾
-
Another day, another cat drawing. This time our more blocky version of a feline fellow creature. Sketch in ibisPaint X and final drawing in Commodore 64 multicolor bitmap (160 x 200 resolution, 16 colors). If I could, I’d knit him a cozy sweater.
🐱🎨👨💻🕹️👾

-
It’s always good to have a firm mental picture of one’s (artistic) process, as to not get bogged down by the details. I’ve updated the C64 multicolor illustration I did yesterday, and separated it into 4 “colors”:
- background color 0 (white)
- ditto 1 (black)
- ditto 2 (red)
- other colors